Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)
Hypoglycemia is the medical term for low or lack of blood glucose. 4.0 mmol/L or less has been described low blood glucose. According to the McKellar specifications, a low blood glucose level in fragile elderly persons may be less than 6.0 mmol/L. At times, it is referred to as “a hypo.”
Some of the most common reasons of hypoglycemia are:
Medication:
If used improperly or in excess, different medicines, including insulin along with other oral diabetic treatments, can drop blood sugar too much.
Meal skipping or improper eating:
If you use blood sugar-lowering medicines, you may have a decrease in blood sugar levels as a result of either of these routines.
Increased physical activity:
Increasing your physical activity can help reduce blood sugar levels, particularly if you don’t change your diet or medication as required.
Alcohol consumption:
Alcohol can cause this by affecting with your liver’s capacity to release stored glucose into your bloodstream, especially when taken in excess or on an empty stomach.
Medical conditions:
A number of illnesses can lead to it by interfering with the body’s capacity to control blood sugar, including kidney diseases, adrenal gland abnormalities, and pancreatic tumors.
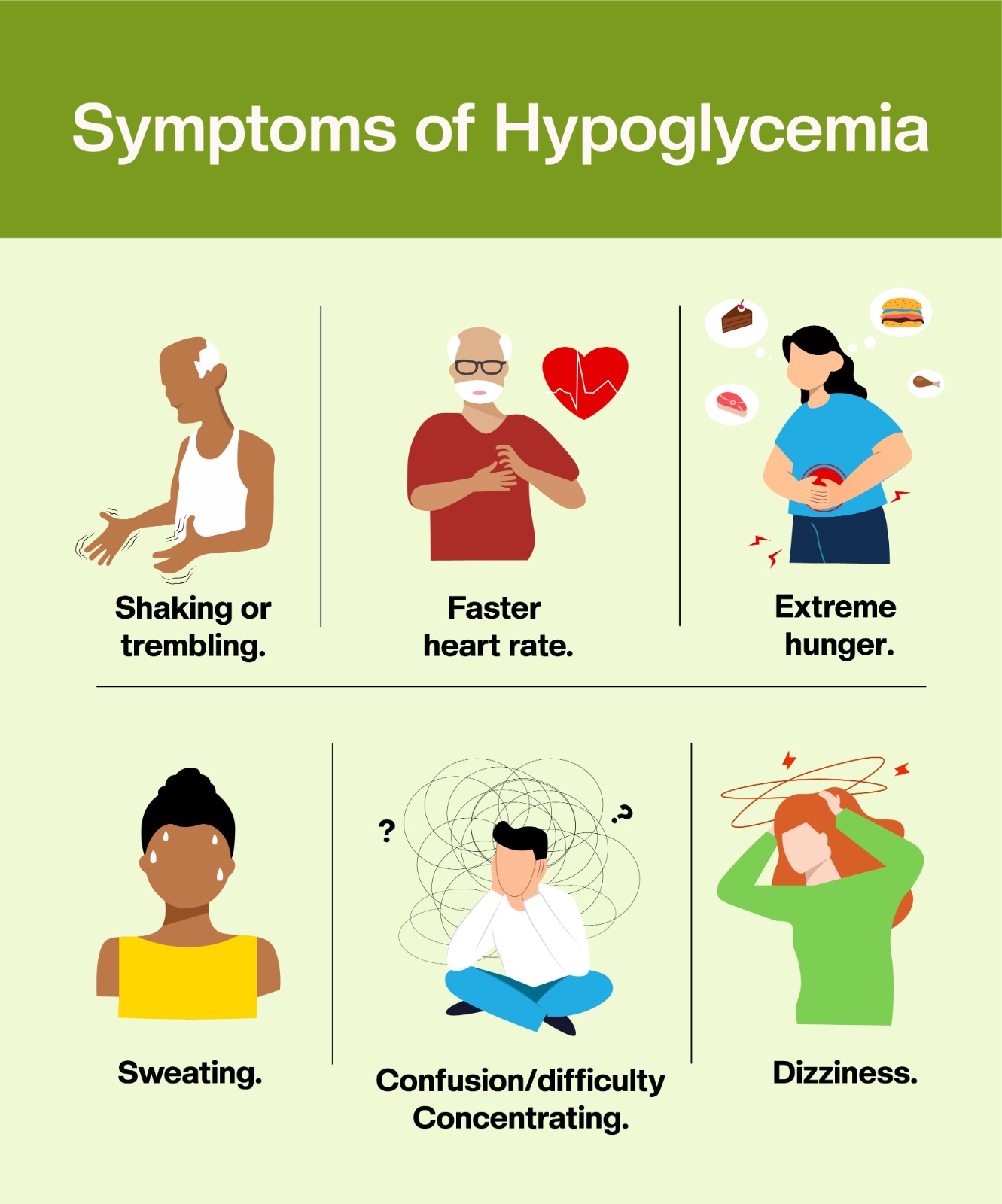
Symptoms of hypoglycemia:
Depending on how low and how rapidly your blood sugar levels fall, it can cause different symptoms. Basic symptoms and signs consist of:
shakiness
Perspiration (Sweating)
Fast heartbeat
Confusion or difficulty concentrating
Dizziness or lightheadedness
Hunger
Irritability or mood swings
Blurred vision
Weakness or fatigue
Headache
Seizures, coma, and maybe death can result from severe hypoglycemia if treatment is not given. In order to rapidly increase blood sugar levels, managing it usually involves intake of fast-acting carbs, such as fruit juice or glucose pills. In rare cases, immediate medical care or glucagon injections could be required. Eating balanced meals, keeping an eye on blood sugar, and changing dosages of medicines as necessary under the direction of a medical expert are all important strategies for prevention.
Natural treatment for Hypoglycaemia:
Making changes in your diet along with certain foods and herbs that can help control blood sugar are important parts of naturally managing it. Here are a few natural methods to keep in mind on:
Dietary modifications:
Pay attention to eating a well-balanced diet rich in fiber, protein, complex carbs, and healthy fats. Stay careful of processed foods and sugars that are refined since they might result in blood sugar rises and falls. Choose whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and healthy fats like those in avocados, nuts, and seeds in place of processed foods.
Regular meals and snacks:
To keep your blood sugar levels stable throughout the day, eat regular meals and snacks. A long period without food might cause blood sugar levels to fall drastically.
Portion control: Control the amount you eat to avoid overeating, which can result in a rise and then drop in blood sugar levels.
Include protein with meals:
Eat protein with your meals to help prevent fast rises and falls in blood sugar levels. Protein slows down the absorption and digestion of sugars and carbohydrates.
Stay hydrated:
To help maintain hydration and improve overall wellness, drink lots of water throughout the day. Dehydration can worsen hypoglycemia symptoms and have an impact on blood sugar levels.
Regular physical activity:
Regular exercise, such as cycling, swimming, or walking, can help control blood sugar levels and enhance insulin sensitivity. When exercising, though, keep a careful eye on your blood sugar since long or extreme physical activity may result in hypoglycemia.
Herbal supplements:
Study has been done on the possible uses of a few herbs and supplements to help control blood sugar. Cinnamon, fenugreek, bitter melon, chromium, and the herb gymnema sylvestre are a few examples. Before beginning any new supplement treatment, you should see a physician, especially if you have any underlying health issues or are currently taking medicine.
Stress management:
Since long-term stress raises blood sugar, performing activities that relieve stress like yoga, tai chi (Tai Chi, often referred to as Taijiquan or Tai Chi Chuan, is an ancient Chinese martial art that has gained popularity as a mind-body workout and meditation method.) deep breathing exercises, or mindfulness meditation may benefit overall health and blood sugar control.
Adequate sleep:
Sufficient sleep may affect the hormones that control blood sugar, so try to get seven to nine hours of good sleep every night.
Regular monitoring:
Keep a close eye on your blood sugar, especially if you have diabetes or are at risk for this illness. You may use this analyze changes and modify your diet and way of life as necessary.
While using these natural methods for controlling this illness might be helpful, it’s essential to work along closely with your healthcare medical professional to create a complete treatment plan that is specific for you. They may provide you specific guidance and track how you progress over time.